Behind-the-Scenes at a Distillery in Galveston: Tours and Tastings
Behind-the-Scenes at a Distillery in Galveston: Tours and Tastings
Blog Article
Distillery Dynamics Revealed: a Trip Through the Science and Art of Spirits Production
As the drapes are withdrawed on the complex globe of distillery dynamics, an interesting world emerges where scientific research and art converge to develop the spirits we savor. Behind the closed doors of distilleries exist secrets waiting to be unwinded, from the thorough chemistry of distillation to the delicate dance of yeast in fermentation. The marriage of custom and innovation in spirits production reveals a tapestry woven with strings of workmanship and technical advancements. Join us on a journey with the heart of purification, where each decrease of spirit narrates of proficiency and enthusiasm, guaranteeing a much deeper understanding of the alchemy that changes grains and fruits right into the liquid gold we raise in a salute.
The Chemistry of Distillation
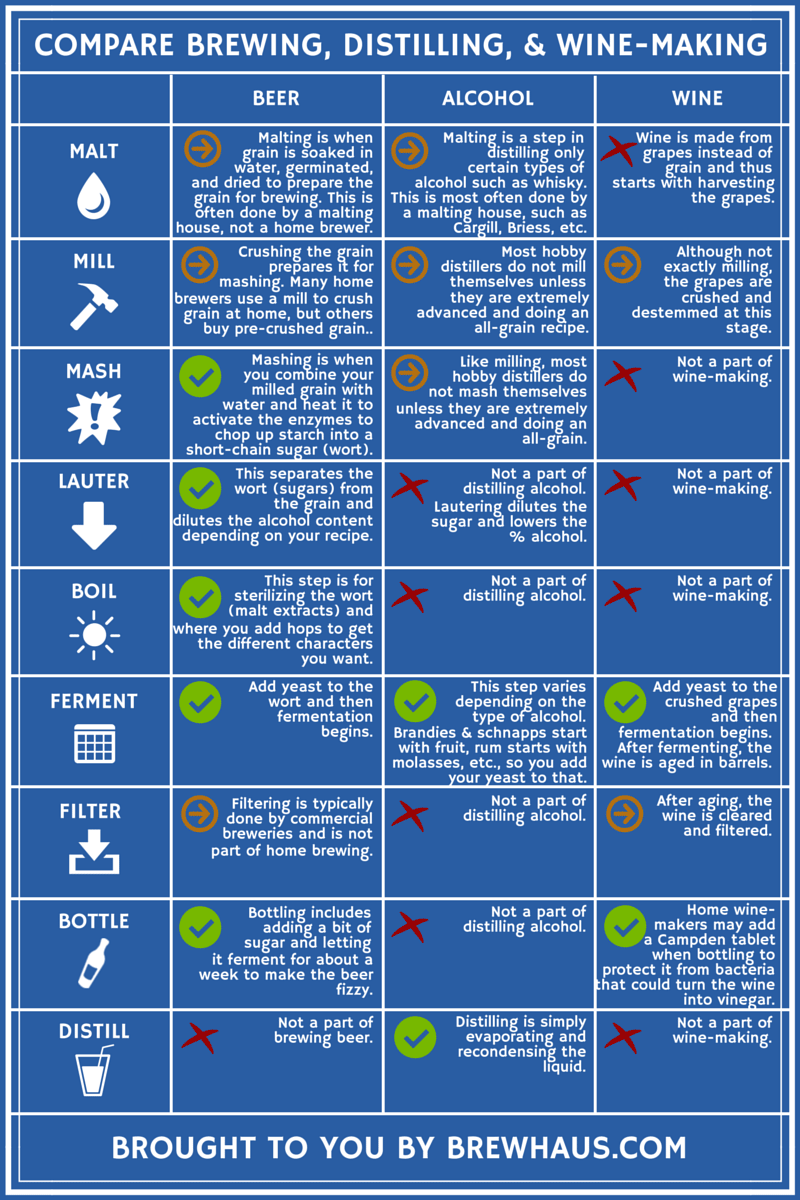
The chemistry of purification, a basic procedure in the manufacturing of spirits, entails the splitting up of components based on their different boiling factors. This procedure depends on the concept that each element in a fluid mixture has an unique boiling point, enabling their individual extraction. When heat is put on the combination, the component with the most affordable boiling point will certainly evaporate initially, rising through the still and at some point condensing back into liquid form. This distilled fluid, called the "heart cut," contains the wanted alcohol web content and flavor compounds.
During distillation, 3 primary fractions are acquired: the "heads," which contain unpredictable substances and higher alcohols that can be harmful if consumed in large amounts; the "hearts," the treasured section with the preferred ethanol and flavor account; and the "tails," which consist of heavier compounds and fusel alcohols. Experienced distillers need to meticulously monitor the temperature level and circulation prices to separate these portions properly, making certain a high-grade final item. The chemistry of purification is a delicate interaction of heat, vaporization, and condensation that transforms an easy fluid mixture into a facility and refined spirit.
Artisanal Craftsmanship in Spirits Making
In the middle of the globe of spirits manufacturing, artisanal craftsmanship plays an essential role in elevating the quality and personality of distilled beverages (Distillery in Galveston). Artisanal craft distillers focus on small-scale, hands-on production approaches, frequently utilizing traditional methods that have actually been given via generations. These devoted craftsmen and ladies focus on top quality over quantity, paying precise focus to every step of the distillation procedure
Artisanal workmanship in spirits making involves a deep understanding of the raw materials utilized, such as fruits, grains, or botanicals, and just how their characteristics influence the end product. From picking the finest components to meticulously keeping an eye on purification, aging, and fermentation, artisans infuse their spirits with passion and experience.
Furthermore, artisanal craft distillers often embrace trial and error and technology, pressing the borders of standard spirits production. They may present distinct taste profiles by incorporating locally sourced ingredients or making use of imaginative aging techniques. This commitment to creative thinking and excellence cause spirits that are not just of extraordinary high quality however also showcase the artistry and originality of the distiller.
Advancements in Aging Methods
One famous advancement acquiring traction is using smaller barrels for aging spirits. By raising the surface area area-to-volume proportion, smaller sized barrels present tastes extra rapidly, causing a more extreme growth process. This strategy is specifically preferred amongst craft distillers seeking to generate top notch spirits in a shorter duration.
Additionally, distillers are significantly turning to different wood kinds, such as cherry or acacia, to impart unique tastes to their aged spirits. These non-traditional timbers offer an one-of-a-kind flavor account, establishing their products apart in an open market.
In addition, developments in modern technology have made it possible for distillers to explore sped up maturing methods, such as ultrasound or temperature level and pressure variants. These strategies enable exact control over the aging procedure, resulting in ingenious taste accounts that push the limits of typical spirits production.

The Function of Yeast in Fermentation
An important component of the fermentation procedure in distilling is the role played by yeast. Yeast, a single-celled microbe, is vital in converting sugars right into alcohol and carbon dioxide throughout fermentation. In the context of distilling spirits, yeast plays an essential duty in the production of ethanol, which is the key alcohol in the majority of liquors.
Yeast achieves this via the process of anaerobic respiration, where it metabolizes sugars such as glucose and fructose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. Different strains of yeast can present one-of-a-kind tastes and scents to the last spirit, contributing to the complexity and personality of the distilled product. Distillers carefully choose yeast stress based upon their wanted flavor account and fermentation features.
The fermentation procedure can last anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on aspects such as yeast pressure, sugar, and temperature material. Surveillance and regulating the fermentation procedure are necessary to make sure ideal yeast activity and alcohol manufacturing. In general, yeast is a basic gamer in the alchemical transformation of raw active ingredients into the spirited elixirs taken pleasure in by consumers worldwide.
Lasting Practices in Distilleries
In the modern-day distilling sector, applying lasting practices has ended up being a pressing top priority for distilleries seeking try these out to reduce their environmental impact and ensure long-lasting viability. Distilleries are progressively acknowledging the value of adopting environment-friendly actions throughout the manufacturing procedure. One vital facet of sustainability in distilleries is water preservation. Distilleries call for substantial amounts of water for various stages of production, and implementing water recycling systems or making use of rainwater harvesting methods can significantly decrease water usage and decrease the distillery's general environmental impact.
Distilleries are exploring ingenious methods to repurpose byproducts such as spent grains or distillation deposits, transforming waste into sources via methods like pet feed production or composting. By accepting lasting techniques, distilleries can not only lessen their environmental influence however likewise charm to ecologically aware customers and add to a more sustainable future for the market.
Verdict
From the chemistry of distillation to the role of yeast in fermentation, distilleries are continuously innovating and experimenting to produce top notch spirits. The combination of custom and development in spirits production highlights the complexity and creativity entailed in this ancient craft.
As the curtains view it are attracted back on the detailed globe of distillery dynamics, an interesting realm arises where scientific research and art converge to create the spirits we appreciate.The chemistry of purification, an essential process in the manufacturing of spirits, involves the splitting up of elements based on their different boiling points.In addition, artisanal craft distillers commonly welcome testing and development, pushing the borders of standard spirits production. In the context of distilling spirits, yeast plays an essential function in the production of ethanol, which is the main alcohol in many alcoholic beverages.
From the chemistry of distillation to the duty of yeast in fermentation, distilleries are continuously trying out and innovating to produce high-quality spirits.
Report this page